Robotic Process Automation presentation slides downbelow
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to the use of software bots to rule-based tasks within business processes. RPA is typically used to automate tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, customer service, and other back-office functions.
RPA bots can be programmed to perform a wide range of tasks, including navigating software applications, manipulating data, copying and pasting information, and even communicating with other systems or software robots. They can work 24/7, without breaks or errors, and can help companies save time and reduce costs associated with manual labor.
RPA is considered a type of “low-code” technology, meaning that it does not require extensive coding knowledge to set up and use. Instead, RPA tools use a visual interface and drag-and-drop functionality to create automation workflows.
How does RPA work?
RPA works by using software robots to automate repetitive, rules-based tasks that would normally be performed by humans. The robots are programmed to follow a set of predefined rules, which are typically based on the steps involved in a particular business process. Here’s a general overview of how RPA works:
1. Identify the process: First, the business process to be automated is identified. This could be anything from data entry and invoice processing to customer service and HR tasks.
2. Create a workflow: Next, a workflow is created that outlines the steps involved in the process. This workflow is typically created using a visual interface provided by the RPA software.
3. Program the bots: The RPA software is then used to program the software robots to perform each step in the workflow. This can involve tasks such as logging into software applications, copying and pasting data, and sending emails.
4. Monitor the bots: Once the bots have been programmed, they can be set to run automatically on a schedule or triggered by certain events. The RPA software also
provides monitoring tools that allow users to track the bots’ progress and identify any errors or issues.
5. Optimize the process: Finally, the RPA process can be optimized over time by analyzing data and making adjustments to the workflow and bot programming as needed. This helps to ensure that the process continues to run smoothly and efficiently.
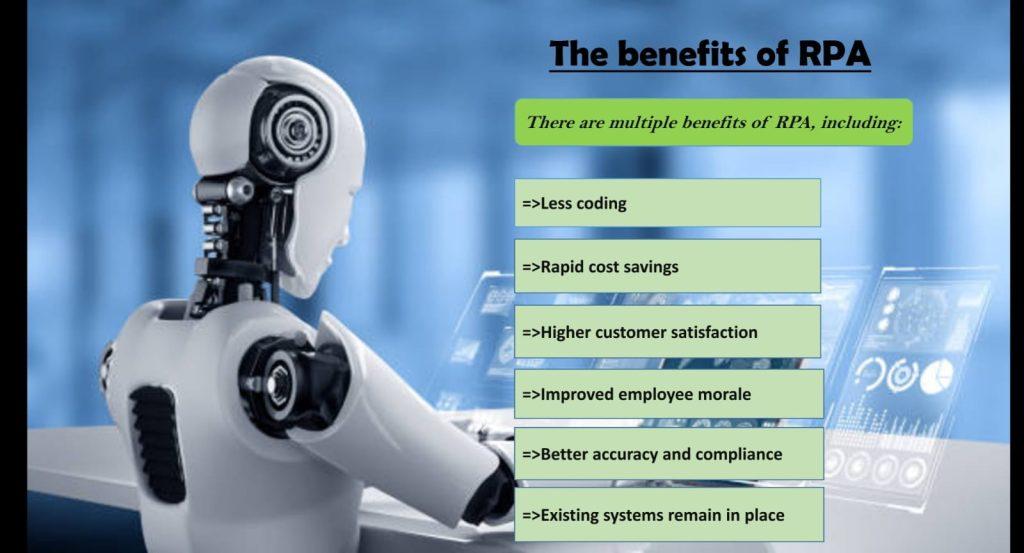
The benefits of RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots (bots) to automate repetitive, rules-based tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities. Here are some benefits of RPA:
- Increased efficiency: RPA can complete tasks faster and more accurately than humans, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. This allows employees to focus on more important tasks.
- Cost savings: Automating tasks with RPA can reduce the cost of labor, as well as the cost of errors and rework. RPA can also be implemented at a lower cost than traditional IT projects.
- Improved accuracy: RPA can reduce errors and improve accuracy, resulting in higher quality outputs and better customer experiences.
- Scalability: RPA can be easily scaled up or down depending on business needs, allowing organizations to quickly respond to changes in demand.
- Increased compliance: RPA can help organizations ensure compliance with regulations and policies by enforcing consistent processes and reducing the risk of errors.
- Improved employee satisfaction: By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, RPA can improve employee satisfaction and reduce burnout.
- Enhanced analytics: RPA can collect and analyze large amounts of data, providing insights that can help organizations make better decisions.
Overall, RPA can help organizations achieve operational excellence and drive business growth by streamlining processes, reducing costs, and improving quality and customer satisfaction.
Robotic Process Automation presentation slides
Downbelow
Download Here :